In the ever-evolving landscape of home heating solutions, technology has continually advanced to offer more efficient, comfortable, and energy-conscious options. Among these innovations, infrared heating stands out as a revolutionary method, harnessing the power of electromagnetic radiation to deliver warmth in an unparalleled and efficient way.
Infrared heaters operate by directly heating objects through ***radiant heat transfer. This efficient method ensures a comfortable warmth without the need for air circulation. These heaters offer energy-efficient and customized heating solutions for both residential and commercial environments. In fact, thanks to its direct heating method, infrared heating systems can be up to 30% more energy-efficient than conventional heating methods.
Table of Contents
What is Infrared Heating?
Understanding the Energy Efficiency of Infrared Heaters
Can Infrared Heat Be Used To Heat A Home?
What About Industrial & Commercial Application?
The PowerBoard Infrared Ceiling Heating System
In this article, we embark on a journey into the intriguing realm of infrared heating systems, unveiling its fundamental principles, advantages, and versatile applications.
What is Infrared Heating?
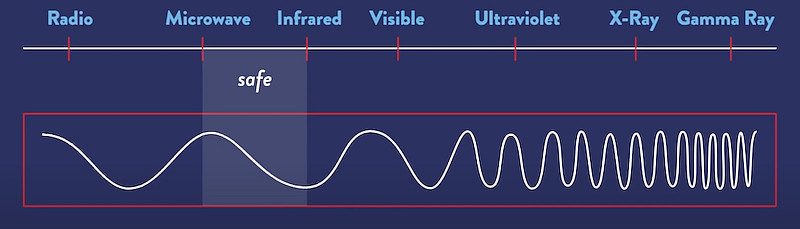
At its core, infrared heating operates on the principle of infrared radiation powered by electricity. This type of electromagnetic radiation falls within the electromagnetic spectrum, lying just beyond the visible light spectrum.
Unlike traditional heating methods that rely on convective or conductive heat transfer, infrared heating directly emits electromagnetic waves that transfer energy in the form of heat when absorbed by objects or surfaces (in other words, infrared is a form of radiant heating). These objects/surfaces then in turn radiate heat as well, leading to an even warmer sensation from your surroundings.
So, How Do Infrared Heaters Work?
Infrared heaters work by emitting electromagnetic radiation in the form of infrared light, which is part of the electromagnetic spectrum with wavelengths longer than visible light (invisible to the human eye) but shorter than microwaves. This radiation is absorbed by objects and surfaces in its path, heating them directly.
- The heart of an infrared heater is the heating element, which can be made of various materials, such as quartz, ceramic, or metal coils (or in our case, carbon fibers!). This element is electrically powered and designed to resist the flow of electricity, which generates heat. When electricity flows through the heating element, it becomes hot due to its resistance to the electrical current.
- When the heating element reaches a high temperature, it emits electromagnetic waves in the infrared spectrum. These waves are commonly referred to as infrared radiation. The specific wavelength emitted can vary depending on the design of the heating element. But elements that reach 50-60°C surface temperature emit in the 6-15um range!
- Infrared heaters utilize a mechanism known as radiant heat transfer. Unlike convection heaters that warm the surrounding air and rely on the circulation of warm air to heat a space or area, radiant heaters heat objects and surfaces directly through the emission of infrared radiation.
Infrared Heating Generates Sun-Like Warmth!
Infrared heaters, commonly in the form of heating panels, units or films, emit infrared radiation that travels in straight lines until it encounters an object or surface. Upon contact, the energy is absorbed and then re-radiated as heat, creating a comfortable and consistent warmth.

This radiant heat transfer is akin to the feeling of basking in the sun’s warmth, where you directly feel the heat on your skin even though the air temperature might be cooler. A common critique of radiant systems can be that they lead to certain temperature asymmetries, but through intelligent project design and placement of the radiating elements, this can easily be avoided!
Optimal Thermal Comfort Tailored to Human Physiology
Delving into solar influence, it becomes evident that life as we know it owes much to the sun. It follows, then, that our biological systems would naturally resonate with the type of warmth emitted by the sun – infrared radiation – which our bodies both absorb and emit.
Thus, when we absorb heat from our surroundings, we experience a comforting warmth, while the sensation of cold arises when we lose heat radiatively.
Essentially, our physiological response favors infrared heating over other methods, such as heating the air. Reflecting on our ancestral past, during eras when fire was our primary source of warmth, our shelters often absorbed and retained heat from the flames, subsequently radiating it back to us even after the fire had subsided. So doesn’t it make sense to try and replicate this in our own homes?
Understanding the Energy Efficiency of Infrared Heaters
One of the standout advantages of this type of heat source is its exceptional efficiency. Traditional heating methods, such as forced-air systems, often lead to heat loss due not only to increased ventilation heat loss attributed to the high air temperature, but also just by the nature of air being fundamentally an insulative material and thus needing a larger amount of heat energy to increase its temperature by 1 degree!
In contrast, infrared heaters are designed to heat objects and surfaces directly, often creating a warm, comfortable environment at lower air temperatures (often 1 degree lower than convective heating solutions), leading to decreased heat loss and more energy savings!
Can Infrared Heat Be Used To Heat A Home?
The short answer as to whether infrared heaters can be used for the home is a resounding “YES”! However, using infrared heaters to the fullest potential will depend on several factors such as is your home large? How many people reside in the home? How high are the ceilings?
All these questions have to be factored in before deciding the number and size of panels required. In short, like any heating system, some calculations are in order.
Our guide on calculating coverage area for maximum infrared efficiency, will provide detailed insights into determining the number of panels needed for various room sizes, along with key considerations to ensure effective heating.
Here are other factors that infrared heaters can do for your home:
#1 The Zoned Heating Method
Infrared heating also offers the benefit of zoned heating, allowing you to target specific rooms/areas for heating, avoiding the energy wastage associated with heating an entire house when you’re only using a couple of rooms! This level of control is especially valuable in larger spaces or homes with varying heating preferences. For example, you might not need as much heat in the kitchen area as you do in the bathroom. On top of this, human comfort temperatures vary, so two people can reside in one room and experience a temperature that suits them.
This combined with a smart home control system gives infrared heating solutions the possibility of being the most energy efficient heating system on the market!
#2 Safety & Increases Well-Being!
Infrared heating stands out not only for its efficiency but also for its health and safety benefits, addressing the question: is FAR infrared heating safe for use? Unlike traditional heating methods that can circulate dust and allergens, infrared heaters are safe, as they do not rely on air movement, resulting in cleaner and healthier indoor air quality.
What About Industrial & Commercial Application?
The versatility of infrared heating extends to its applications. From residential spaces to commercial buildings, and even outdoor settings, infrared heating finds its utility in various scenarios. It’s commonly used for indoor heating, including living spaces, bedrooms, bathrooms, and even basements.

In commercial settings, it’s embraced for heating offices, warehouses, restaurants, and even hospitals as a way of tackling the spread of airborne infections. Additionally, outdoor seating areas, patios, and even driveways benefit from the targeted warmth of infrared heaters.They offer a range of options tailored to diverse needs and preferences. They can be categorized into three main types:
1. High-Output Industrial Infrared Heaters: These units operate at a surface temperature of 150°C or higher using **Near infrared heat (NIR) and are designed for heating larger spaces or areas with substantial heating requirements. They typically deliver higher wattage outputs, resulting in increased heat emission. They are commonly employed in commercial settings such as warehouses, showrooms, or factories, where maintaining a specific constant temperature is required.
2. Residential-Grade Medium-Capacity Heaters: These panels maintain a surface temperature between 90°C and 110°C, making them more suitable for residential applications or smaller spaces that require targeted heating.
3. Embedded Infrared Panel Units: These units maintain a surface temperature of 50°C to 60°C using *Far infrared heat (FIR) and are well-suited for medium to large spaces that demand uniform heat distribution and an inconspicuous heat source.
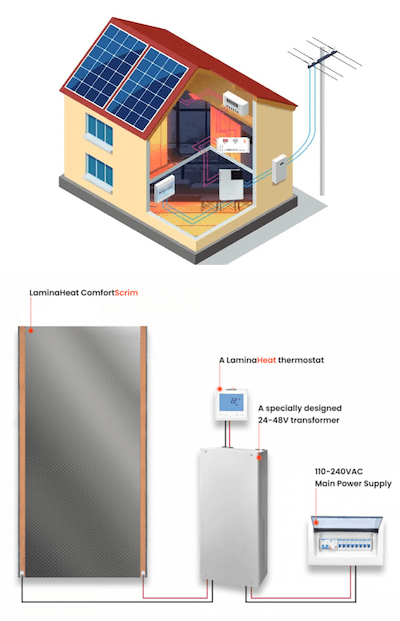
Innovation in Action: The PowerBoard Infrared Ceiling Heating System
As the demand for energy-efficient and comfortable heating solutions grows, innovation has given rise to advanced systems like The PowerBoard Infrared Heating System. This revolutionary system goes beyond traditional panel heaters by utilizing LaminaHeat’s Carbon Fibre Full Surface Heating Films. This technology ensures even heat distribution, increased efficiency, and seamless integration into architectural spaces.
In summary, infrared heating stands as a testament to the marriage of science and comfort. By harnessing the principles of infrared radiation, it provides an efficient, personalized, and health-conscious approach to home heating. As the world seeks more sustainable and effective solutions, infrared heating remains a beacon of warmth in the evolving landscape of modern living. Whether you’re looking to upgrade your home’s heating system or seeking innovative solutions for commercial spaces, the radiant embrace of infrared heating offers a path to a cozier and more energy-efficient future.
If you’re still curious on how infrared heating works, feel free to watch the video below introducing it in more detail!
* Far Infrared: The longest wavelength in the infrared spectrum. It therefore produces lower temperatures and is therefore ideal for home heating!
** Near Infrared: The shortest wavelength in the spectrum and it is used for more intense heating solutions, such as in commercial or industrial environments.
*** Radiant Heat: Radiant heat refers to the transfer of heat energy from one surface to another through electromagnetic waves.